The Future in PFAS Waste Management Methods for Environmental Protection
The Future in PFAS Waste Management Methods for Environmental Protection
Blog Article
Your Overview to PFAS Treatment Technologies and Advantages
The occurrence of PFAS contamination in water resources demands an extensive understanding of offered treatment modern technologies. Different methods, such as turned on carbon filtering, ion exchange systems, and progressed oxidation procedures, present distinctive benefits in dealing with these persistent contaminants. Each technology not only targets certain PFAS substances yet likewise plays a crucial duty in boosting general water high quality and safeguarding ecological stability. As areas come to grips with the effects of PFAS direct exposure, the option of an appropriate treatment method comes to be increasingly vital, motivating a more detailed examination of these technologies and their particular advantages.
Understanding PFAS Contamination
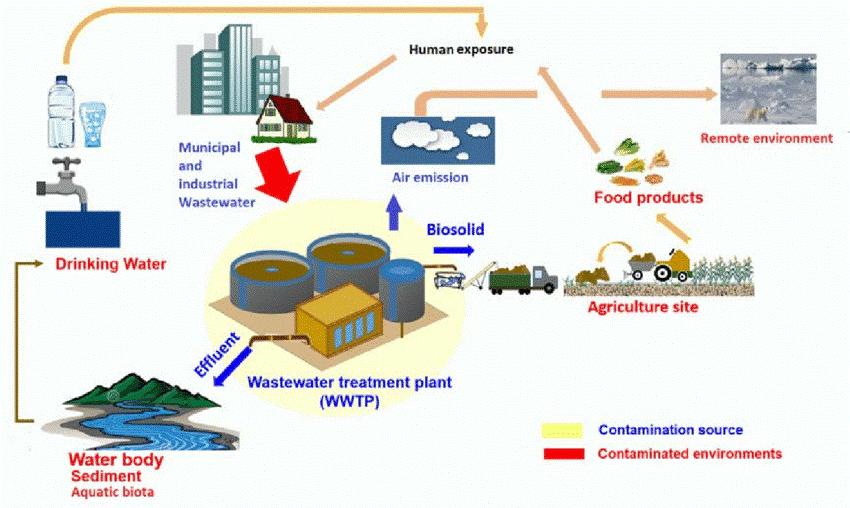
Comprehending PFAS contamination is crucial for resolving its prevalent influence on environmental and human health (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of synthetic chemicals commonly utilized in various industrial and customer items because of their water- and grease-resistant properties. Typically located in firefighting foams, non-stick cookware, and water-repellent fabrics, PFAS have entered the environment through production procedures, wastewater discharges, and seeping from landfills
When released, these substances persist in the environment, causing extensive contamination of dirt and water resources. Their one-of-a-kind chemical framework, identified by strong carbon-fluorine bonds, makes them resistant to deterioration, leading to a phenomenon referred to as "permanently chemicals." As a result, PFAS can build up in the human body and the food chain, potentially causing adverse wellness results, including immune system disruption, developmental concerns, and a raised risk of particular cancers cells.
Regulatory firms and wellness companies are progressively recognizing the value of PFAS contamination, triggering efforts to keep an eye on, analyze, and reduce its effects. Understanding the paths of PFAS contamination is necessary for informing public plan and creating efficient strategies to secure both ecological and human health and wellness.
Overview of Therapy Technologies
Different treatment innovations have actually been developed to attend to the obstacles positioned by PFAS contamination in water and soil. These innovations can be broadly categorized right into numerous categories, each with its special mechanisms and performance in removing PFAS compounds.
One prominent approach is ion exchange, which utilizes resin materials to capture and eliminate PFAS from contaminated water. An additional innovation, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), uses strong oxidants and ultraviolet light to break down PFAS into less damaging compounds.

Turned On Carbon Filtration
Activated carbon filtration is an extensively utilized method for the removal of PFAS from polluted water, understood for its capability to adsorb a broad variety of natural compounds. This innovation utilizes triggered carbon, an extremely porous material with a considerable area, which facilitates the binding of PFAS molecules via physical adsorption. The effectiveness of turned on carbon in getting rid of PFAS is affected by a number of aspects, including the kind of carbon utilized, the get in touch with time, and the concentration of PFAS in the water.
One of the advantages of turned on carbon purification is its versatility; it find out here can be carried out in various setups, such as granular turned on carbon (GAC) systems or powdered turned on carbon (SPECIAL-INTEREST GROUP) systems. GAC systems are typically used in larger-scale applications, while special-interest group can be made use of in smaller sized or temporary configurations. The innovation is fairly easy to run and preserve, making it check available for lots of water therapy centers.
Ion Exchange Systems
Ion exchange systems stand for one more effective strategy for the removal of PFAS from infected water, matching methods like activated carbon filtering. These systems operate the concept of exchanging ions in the water with ions hung on a resin material. Ion exchange materials can be specifically created to target the negatively billed PFAS compounds, properly catching them and permitting cleaner water to go through.
Among the main benefits of ion exchange systems is their ability to get rid of a variety of PFAS, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain versions. This adaptability makes them suitable for numerous applications, ranging from metropolitan water treatment to commercial processes. Furthermore, ion exchange systems can typically attain lower detection restrictions for PFAS contrasted to a few other treatment techniques, thus improving water top quality.
However, it is necessary to monitor and handle the regrowth of ion exchange media, as the performance can decrease in time as a result of saturation. Appropriate maintenance and replacement of the material are crucial for sustaining the system's efficiency. On the whole, ion exchange systems offer a trusted and effective option for PFAS removal, contributing dramatically to safe drinking water requirements and ecological defense.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) utilize effective oxidants to efficiently break down PFAS substances in polluted water. These cutting-edge therapy methods produce extremely responsive types, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can damage down intricate PFAS particles into less unsafe results. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs usually utilize combinations of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, improving the oxidation capacity and enhancing deterioration More about the author effectiveness
The primary advantage of AOPs hinges on their capability to target a broad variety of PFAS compounds, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain versions. This versatility is necessary, as PFAS contamination frequently includes mixes of different compounds with differing chemical frameworks. AOPs can be integrated into existing water therapy systems, making them a practical option for numerous towns and industries.
However, the application of AOPs can be resource-intensive, needing careful factor to consider of operational costs and power consumption. Additionally, while AOPs work in damaging down PFAS, they may not entirely get rid of all results, requiring further therapy actions - m270 pfas treatment. In general, AOPs represent an appealing method for addressing PFAS contamination, contributing to cleaner water sources and boosted public wellness protection

Verdict
Finally, attending to PFAS contamination needs an extensive understanding of available therapy modern technologies. Triggered carbon filtering, ion exchange systems, and advanced oxidation procedures each present distinct advantages for properly eliminating these damaging compounds from water resources. By choosing the suitable technology, communities can boost water high quality, safeguard public health, and reduce the environmental dangers connected with PFAS exposure. Continued study and implementation of these methods are necessary for efficient monitoring of PFAS contamination in impacted areas.
Report this page